I’d like to introduce guest blogger Heather O’Neil of Yorkshire, United Kingdom. She graduated in 1984 with a degree in Art & Textile design and writes a blog on how art therapy can help those living with Alzheimers. Creative Carer
Read how she has used her skills to engage her dear mother in productive and satisfying art projects. Heather and her mum are amazing!
Find more information about art therapy, including simple art projects that both caregivers and loved ones with dementia can enjoy, in chapter 19 of my book “Calmer Waters: The Caregiver’s Journey Through Alzheimer’s & Dementia.” Available wherever fine books are sold. 
By Heather O’Neil
My mum was diagnosed with mixed dementia – Alzheimer’s & Vascular Dementia – in 2012 when she was 82. Since then I have constantly researched how best to cope with the disease and have looked for different ways to stimulate her memory and keep her active, happy and engaged despite her Dementia.
Studies show that Art Therapy stimulates the brain, reduces agitation and creates a sense of accomplishment and purpose. This has been the perfect therapy for my mum as she has always been a very creative person.
She passed on her love of arts & crafts to me and I graduated in 1984 with a degree in Art & Textile design. I have been able to introduce my inherited creativity into my caring and I was called the ‘Creative Carer’ by mum’s memory clinic!
I started our Creative Carer Face Book page a couple of years ago to share our activities & ideas. We now have followers from all over the world and have made some wonderful friends.
www.facebook.com/CreativeCarer
I spend time every morning with my mum and make sure she always engages in some form of artistic activity … from colouring to card making … shell craft to painting stones!


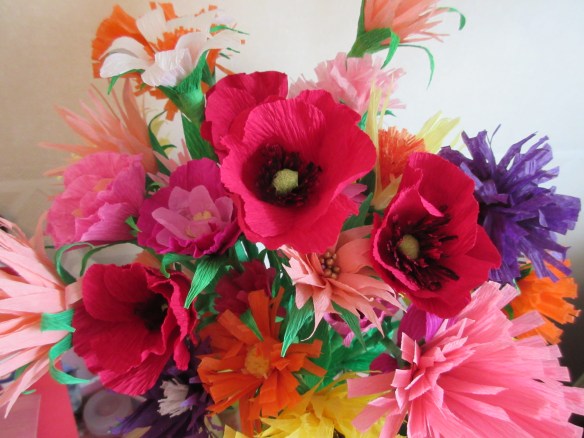
My mum’s favourite hobby is making beautiful crepe paper flowers. This is a craft she enjoyed when she was much younger … I remember wonderful displays in our home when I was growing up so it has been lovely for her to be able to enjoy her flower making once again!
Due to the Alzheimer’s my mum has lost a lot of confidence and she can no longer design and cut out shapes freehand. However, if I supply a cardboard template she is happy to follow the pattern and will sit for hours cutting out pretty petals and leaves. She particularly enjoys covering wooden kebab skewers with long strips of green crepe paper to create the stems! Making the stems is an activity she can do all on her own and she can cover a pack of 100 skewers in an afternoon 😊
Together we glue the stamens and petals to the stems and once she’s done two or three with me, she’s usually able to carry on by herself! Beautiful crepe paper flowers fill the house and are a constant reminder to her that she is wonderfully creative!
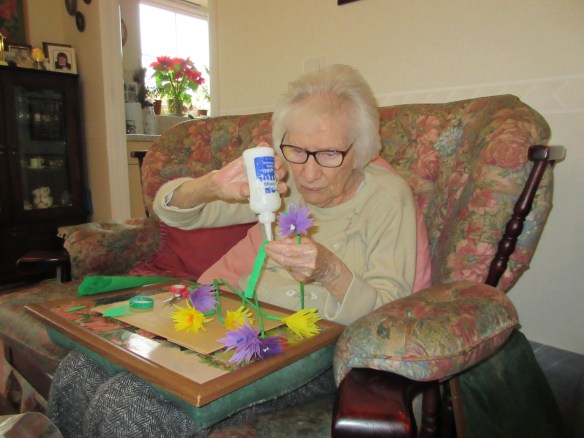


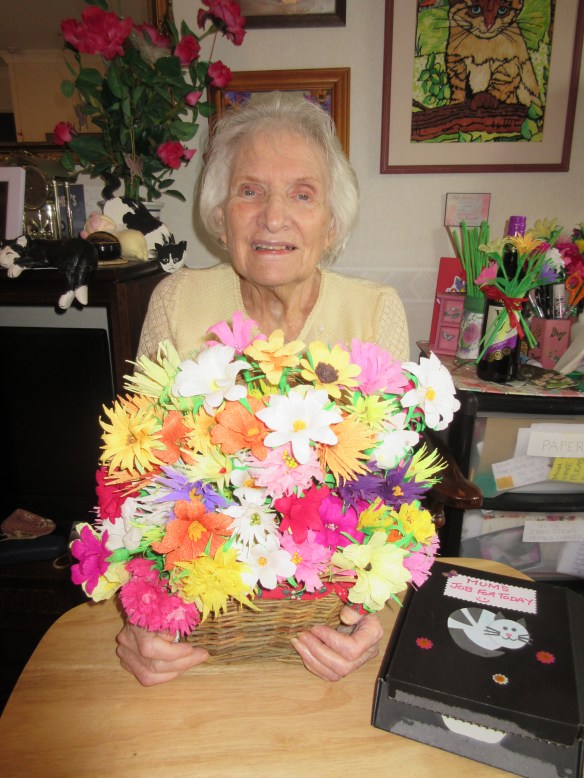
I had the idea to introduce a “Job Box” a few months ago with amazing success! My mum loves to be busy during the day but without me there to encourage and suggest activities she struggled to start any projects. The “Job Box” gives her a reminder of what she can do in the afternoon when I’m not with her. Every day I will leave her a “job” … cutting out petals for example … when I return the next morning the box will be full of her work and she’s always so proud to show me what she’s accomplished.


Mum’s flowers have been greatly admired on our Face Book page and my blog and we have been asked many times if she sells them. With so much stock around thanks to the “Job Box”, I decided to fulfil her ambition of having her own little business!! On the 29th of August 2017 I opened an Etsy shop for her! We pledge to give 25% to the Alzheimer’s Society and already have made over £110 for them!! Mum’s flowers have been shipped all round the world … from the UK to America, Canada and Australia!!! Absolute proof that you are never too old to fulfil your dreams and with a little support and creative encouragement there really can be a future after an Alzheimer’s diagnosis.


http://creative-carer.blogspot.co.uk/2016/06/making-paper-flowers-art-therapy-for.html

 Today is World Alzheimer’s Awareness Day. It’s a good day to repost this important article and to remind people about the book I wrote after caring for my husband who passsed away from younger-onset Alzheimer’s disease seven years ago. The book has helped so many people, which is what my intention was in writing it. “Calmer Waters: The Caregiver’s Journey Through Alzheimer’s & Dementia” contains a treasure trove of information on how to stay connected with your loved one, keep calm, improve immunity, reduce stress and feel happier and healthier. Plus, it includes 20 healing modalities that the caregiver can do alone or with their loved one. Available wherever fine books are sold and on
Today is World Alzheimer’s Awareness Day. It’s a good day to repost this important article and to remind people about the book I wrote after caring for my husband who passsed away from younger-onset Alzheimer’s disease seven years ago. The book has helped so many people, which is what my intention was in writing it. “Calmer Waters: The Caregiver’s Journey Through Alzheimer’s & Dementia” contains a treasure trove of information on how to stay connected with your loved one, keep calm, improve immunity, reduce stress and feel happier and healthier. Plus, it includes 20 healing modalities that the caregiver can do alone or with their loved one. Available wherever fine books are sold and on  It’s sometimes hard to love a family member who has dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. People with dementia can be quarrelsome, uncooperative, negative, whiney, belligerent or combative. They might get their nights and days mixed up, pace the floor for hours, wring their hands non-stop, or cry like a baby. They might ask you the same question twenty times in a row, refuse to budge when you need to get them to an appointment, or refuse to eat what you’ve made for dinner.
It’s sometimes hard to love a family member who has dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. People with dementia can be quarrelsome, uncooperative, negative, whiney, belligerent or combative. They might get their nights and days mixed up, pace the floor for hours, wring their hands non-stop, or cry like a baby. They might ask you the same question twenty times in a row, refuse to budge when you need to get them to an appointment, or refuse to eat what you’ve made for dinner.